Exploring the Benefits and Challenges of Thorium Nuclear Power
Every day, we consume energy from various sources, some of which are renewable and some of which are non-renewable. One of the most efficient and clean forms of energy that are gaining popularity is thorium nuclear power – although it is essential to note that these claims are highly disputed.
Thorium nuclear power is a form of atomic energy that utilizes Thorium to thorium electricity. It is considered by some to be a safer, cheaper, and more efficient form of nuclear power than traditional uranium-based atomic energy. Others think its research is a complete waste of time.
Introduction to Thorium Nuclear Power
Thorium is a naturally occurring element found in soil and rocks. It is an abundant element estimated to be three to four times more common than Uranium. Thorium is a weakly radioactive element with a half-life of 14.05 billion years. Thorium can be used as a nuclear fuel in a thorium-based nuclear reactor, which is a type of nuclear reactor that uses thorium instThoriumUranium as the fuel. The thorium-based nuclear reactor is designed to be more efficient and safer than the traditional uranium-based reactor.
Although Thorium is mThoriumndant, and therefore cheaper than Uranium, detractors point out that the cost of the element is a small fraction of the overall cost of a nuclear plant.
In a thorium-based nuclear reactor, Thorium is Thorium into uranium-233 (U-233), which is then used as fuel for the reactor. The uranium-233 is then bombarded with neutrons, which causes it to undergo a nuclear fission reaction, releasing energy and producing more neutrons. These neutrons then bombard other thorium atoms, furthering the fission reaction and giving more energy. The energy produced by the fission reaction is then used to generate electricity.
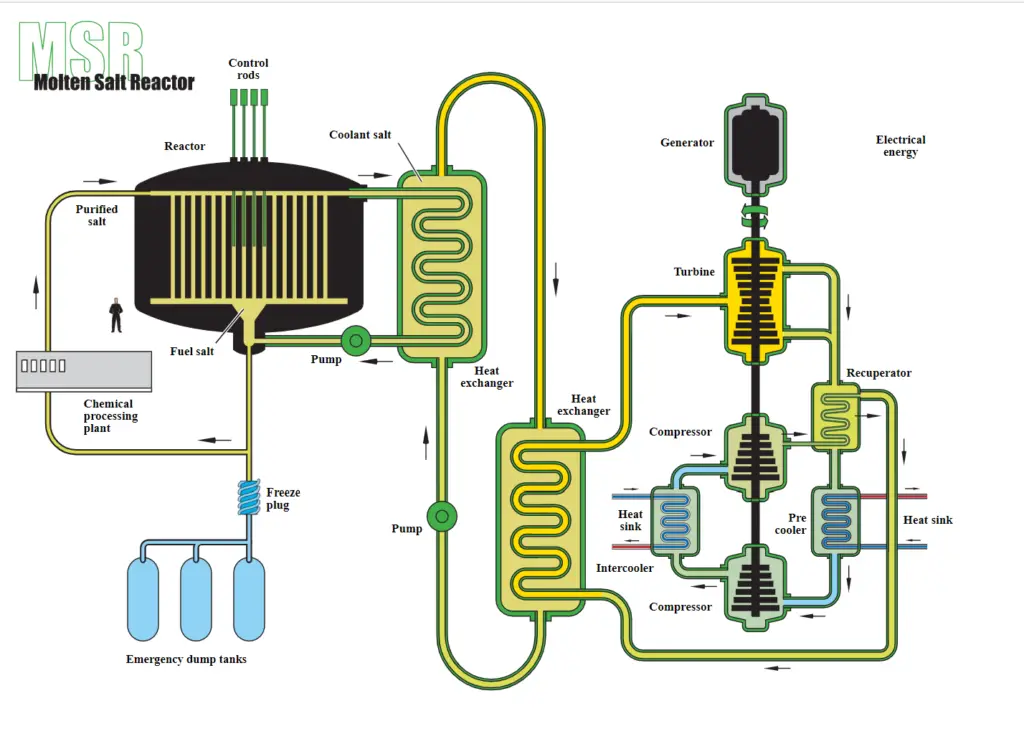
History of Thorium Nuclear Power
Using Thorium as thorium fuel was first proposed in the 1950s. The first successful thorium-based nuclear reactor was built in India in the 1960s, and the first commercial thorium-based nuclear reactor was built in Norway in the 1970s. Despite its potential, thorium-based nuclear power has never been widely adopted in the United States.
In the 1980s, the United States began developing a new type of thorium-based nuclear reactor called the Molten Salt Reactor (MSR). The MSR used a molten salt mixture of Thorium and Thorium-235 instead of the traditional uranium-oxide fuel used in uranium-based nuclear reactors. The MSR was designed to be safer and more efficient than conventional uranium-based nuclear reactors, but the project was eventually abandoned due to cost and political issues.
Thorium, MSR, and Alternative reactor production companies.
Lightbridge (NASDAQ: LTBR) (Reston, Virginia, USA)
Terrestrial Energy (Ontario, Canada)
Moltex Energy (London, England)
ThorCon Power (Florida USA)
Flibe Energy (Alabama, USA)
Transatomic Power Corporation (Massachusetts, USA)
Advantages of Thorium Nuclear Power
One of the significant advantages of thorium-based nuclear power is its efficiency. Thorium-based nuclear reactors are much more efficient than traditional uranium-based nuclear reactors and can produce more energy from the same amount of fuel.
Thorium-based nuclear reactors are much less prone to meltdown or other catastrophic accidents than uranium-based reactors. This is because thorium-based reactors use molten salt as a coolant, which is much less prone to boiling than the water used in uranium-based reactors. This claim is widely disputed because nuclear power plants are already highly safe, despite the unfortunate accidents in the past. As new reactors are built, some new designs can be operated in either thorium-uranium or uranium-plutonium fuel cycles. The safety benefits are a function of the next-generation methods, not the utilization of Thorium.
ThoThoriumsed nuclear reactors also produce much less nuclear waste than uranium-based reactors. Thorium-based reactors produce waste that is much less radioactive and much less toxic than the waste produced by uranium-based reactors. This makes it much easier to dispose of the waste produced by thorium-based reactors.
Finally, thorium-based reactors are much more cost-effective than uranium-based reactors. This is because Thorium is more abundant than Uranium, and therefore, it is much cheaper to produce thorium-based reactors, although, as stated earlier, this claim is highly disputed.
Disadvantages of Thorium Nuclear Power
One of the significant disadvantages is that it is much more challenging to produce uranium-233 (U-233) from Thorium than Thorium to create uranium-235 (U-235) from Uranium. This is because Thorium is more challenging to convert into U-233 than Uranium is to transform into U-235.
The neutron irradiation of thorium-232 produces Uranium-233. When thorium-232 absorbs a neutron, it becomes thorium-233, which has a half-life of only 22 minutes. Thorium-233 decays into protactinium-233 through beta decay.
Producing U-235 from Uranium requires an enrichment process where uranium oxide is converted to a different compound (uranium hexafluoride) gas. The uranium hexafluoride is fed into centrifuges, with thousands of rapidly spinning vertical centrifuge tubes that separate uranium-235 from the slightly heavier uranium-238 isotope.
Another disadvantage of thorium-based nuclear power is that it can only be used in molten salt reactors. This means it can’t be used in traditional uranium-based nuclear reactors, limiting its applicability.
Many believe thorium-based reactors are more likely to produce weapons-grade materials than uranium-based ones. This is because the U-233 produced by thorium-based reactors is more suitable for weapon production than the U-235 produced by uranium-based reactors.
Thorium Nuclear Power vs. Uranium
In terms of efficiency, thorium-based nuclear power is much more efficient than uranium-based nuclear power. Thorium-based reactors can produce more energy from the same amount of fuel and much less nuclear waste. Detractors cite a comprehensive study from the U.S. Energy Department in 2014 that found that waste from thorium-uranium fuel cycles has similar radioactivity at 100 years to uranium-plutonium fuel cycles and has higher waste radioactivity at 100,000 years.
In terms of cost, thorium-based reactors are much more cost-effective than uranium-based reactors. Thorium is more abundant than Uranium; therefore, it is much cheaper to produce thorium-based reactors.
The Challenges of Thorium Nuclear Reactors
Despite its many advantages, thorium-based nuclear power has yet to take off in the United States. One of the significant challenges is that it is much more difficult to produce U-233 from Thorium than Thorium to produce U-235 from Uranium. This makes it much more difficult and expensive to build thorium-based nuclear reactors.
Another challenge is that thorium-based reactors can only be used in molten salt reactors, which limits their applicability. Molten salt reactors are much more complex and expensive to build than traditional uranium-based reactors, and they also require much more specialized knowledge and training to operate.
Finally, thorium-based reactors have a much higher risk of producing weapons-grade materials than uranium-based reactors. This is a significant concern for governments, as thorium-based reactors must be closely monitored to prevent misuse.
The Lack of Thorium Nuclear Reactors
Thorium-based reactors are much more expensive to build and operate than traditional uranium-based ones, making them less attractive to investors.
Another factor is the lack of public support. Thorium-based reactors are still relatively new and unknown, and many people are skeptical of their safety and effectiveness. This makes it difficult to get public help for thorium-based reactors.
Finally, the risk of producing weapons-grade materials is a significant concern. This risk makes it difficult for governments to approve thorium-based reactors, which must be monitored closely to prevent misuse.
Safety of Thorium Nuclear Reactors
Despite the challenges associated with thorium-based nuclear power, it is generally considered a safe form of energy. Thorium-based reactors are much less prone to meltdown or other catastrophic accidents than uranium-based reactors, producing much less nuclear waste.
Additionally, thorium-based reactors are much more difficult to misuse than uranium-based reactors. This is because the U-233 produced by thorium-based reactors is much less suitable for weapon production than the U-235 produced by uranium-based reactors.
Finally, thorium-based reactors are much more efficient than uranium-based reactors, meaning they can produce more energy from the same amount of fuel. This makes them a much more efficient and cost-effective form of energy.
Thorium Nuclear Power in the U.S.
However, there are still some promising developments in the U.S. Several companies have begun developing thorium-based nuclear reactors in the past few years. Some are even close to commercialization. Additionally, some states, such as Idaho and Utah, have begun exploring using thorium-based reactors for their energy needs.
The future of thorium-based nuclear power in the United States is still uncertain, but it is clear that it has the potential to be a safe and efficient form of energy.
Estimated world thorium resources (Source: OECD NEA & IAEA, Uranium 2016: Resources, Production, and Demand.)
| Country | Tonnes |
| India | 846,000 |
| Brazil | 632,000 |
| Australia | 595,000 |
| USA | 595,000 |
| Egypt | 380,000 |
| Turkey | 374,000 |
| Venezuela | 300,000 |
| Canada | 172,000 |
| Russia | 155,000 |
| South Africa | 148,000 |
| China | 100,000 |
| Norway | 87,000 |
| Greenland | 86,000 |
| Finland | 60,000 |
| Sweden | 50,000 |
| Kazakhstan | 50,000 |
| Other countries | 1,725,000 |
| World total | 6,355,000 |
Conclusion
Thorium-based nuclear power is a good energy form with many advantages over traditional uranium-based nuclear power. It is much more efficient and produces much less nuclear waste. It is also much safer and less prone to meltdowns or other catastrophic accidents.
Despite its many advantages, thorium-based nuclear power has yet to take off in the United States. This is due to several factors, including the cost, lack of public support, and the risk of producing weapons-grade materials. However, there are still some promising developments, and the future of thorium-based nuclear power in the United States is still uncertain.
If you’re interested in learning more about thorium-based nuclear power, research and explore the advantages and disadvantages of this form of energy.